Real-world Dataset
Our dataset consists of 120k real-world frames with sparse LiDAR for evaluation
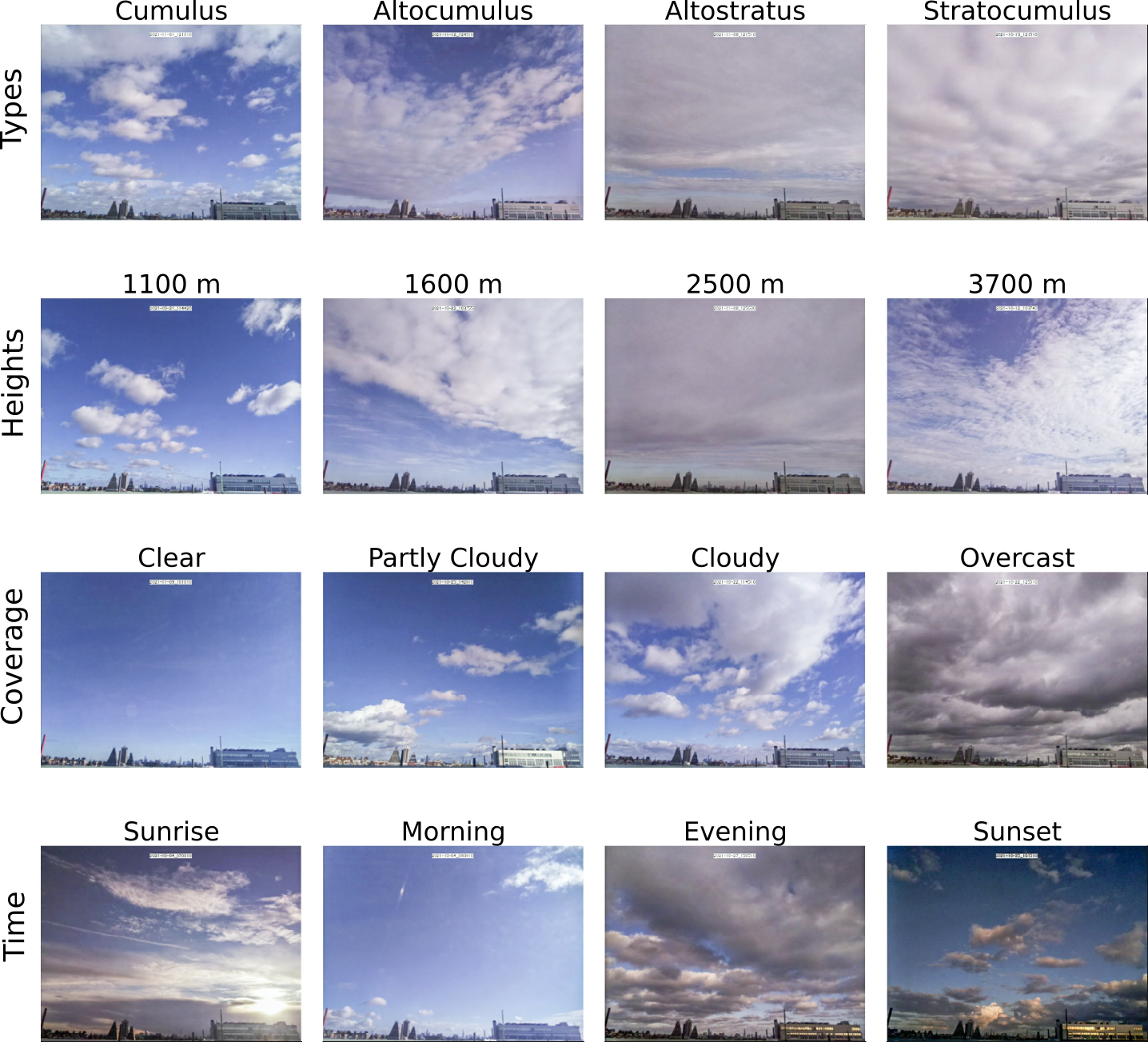

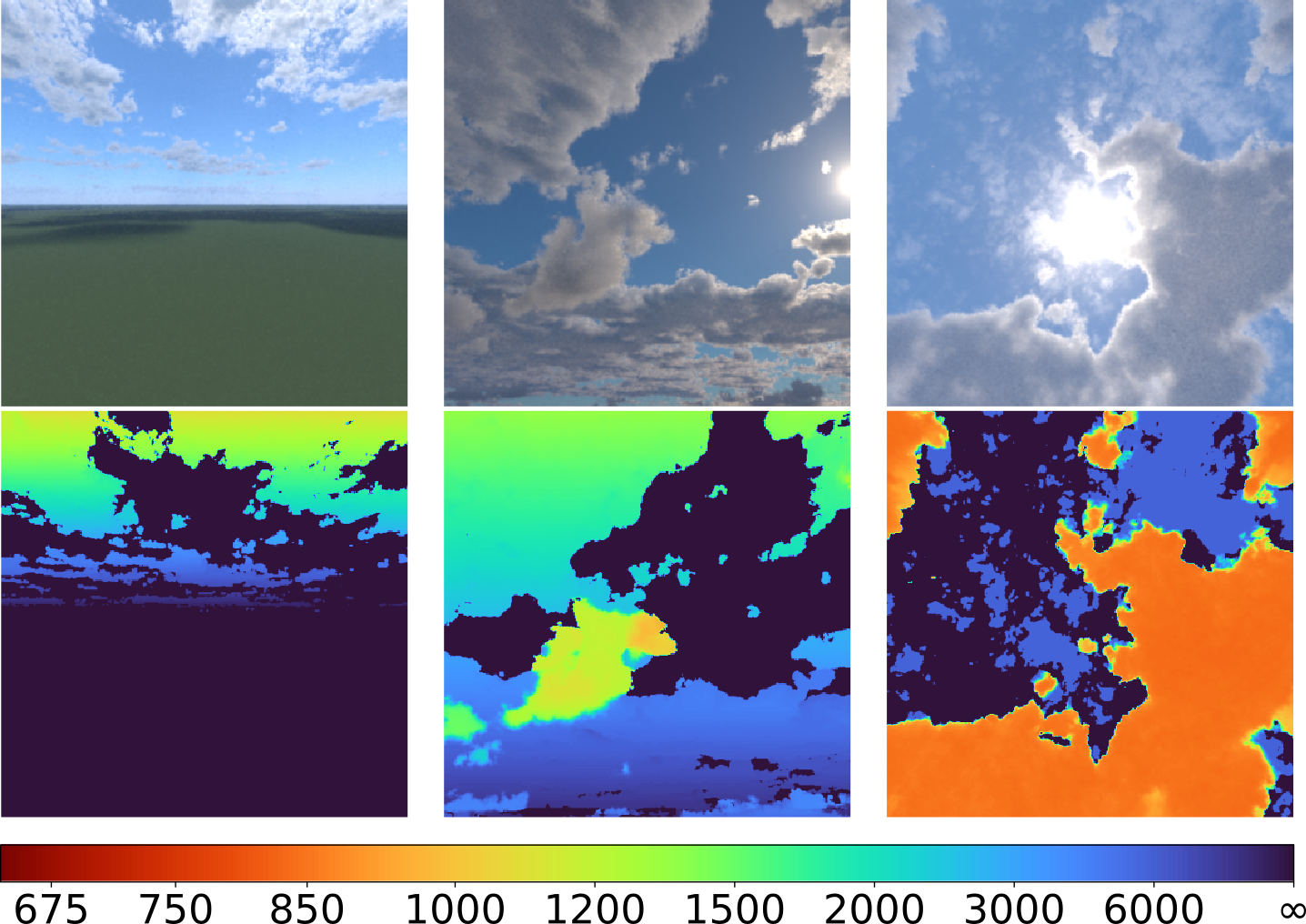
A stereo camera + LiDAR dataset for atmospheric clouds
Obtaining accurate measurements of clouds is a critical problem in atmospheric physics, as accurate modeling of cloud properties allows us to better understand and predict climate change. Stereo camera networks have shown promise in obtaining such measurements, being able to reconstruct detailed cloud fields over multi-km domains. However, previous studies on cloud stereo depth estimation have been limited to using traditional (non-learned) matching techniques, due to the absence of suitable training datasets for this challenging domain. In this work, we present a novel dataset (Cloud-Stereo) specifically tailored for cloud depth estimation. The Cloud-Stereo dataset includes: 1) a synthetic dataset for training, comprising 3000 stereo pairs and simulated dense LiDAR depth data, and 2) a high-accuracy real-world dataset consisting of frames acquired from a stereo camera and Doppler Aerosol LiDAR for testing. Using our dataset we benchmark existing learning and non-learning based stereo depth estimation approaches, and demonstrate that fine-tuning on our dataset can lead to significant accuracy improvement for learned methods. We believe this dataset will enable the training of future, more accurate, methods for cloud field reconstruction, enhancing a unique measurement capability for developing and evaluating atmospheric models.

@inproceedings{Lin_2025_BMVC,
author = {Jacob Lin and Edward Gryspeerdt and Ronald Clark},
title = {Cloud-Stereo: A Dataset and Benchmark for Reconstructing Atmospheric Clouds from Stereo Images},
booktitle = {36th British Machine Vision Conference 2025, {BMVC} 2025, Sheffield, UK, November 24-27, 2025},
publisher = {BMVA},
year = {2025},
url = {https://bmva-archive.org.uk/bmvc/2025/assets/papers/Paper_835/paper.pdf}
}